Implementation of I2C master sending data API:Part 3
Send the address of the slave with r/w bit: Next step is to send the address of the slave with read/write bit set to 0.
- Create a helper function I2C_ExecuteAddressPhase and send the base address of the peripheral and slave address as a parameter of it, as shown in Figure 1. This API can be kept private to the driver since it is just a helper function.
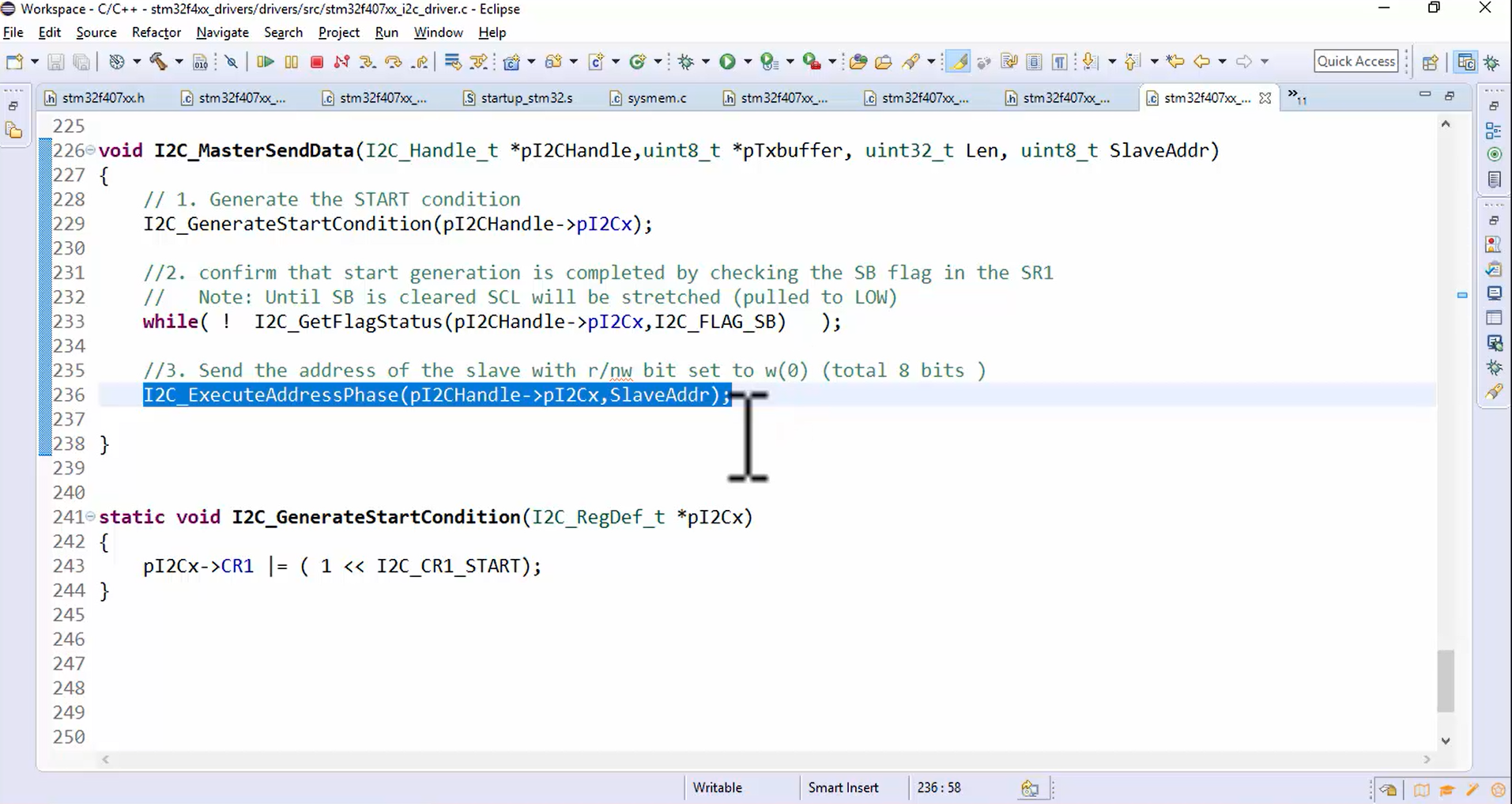
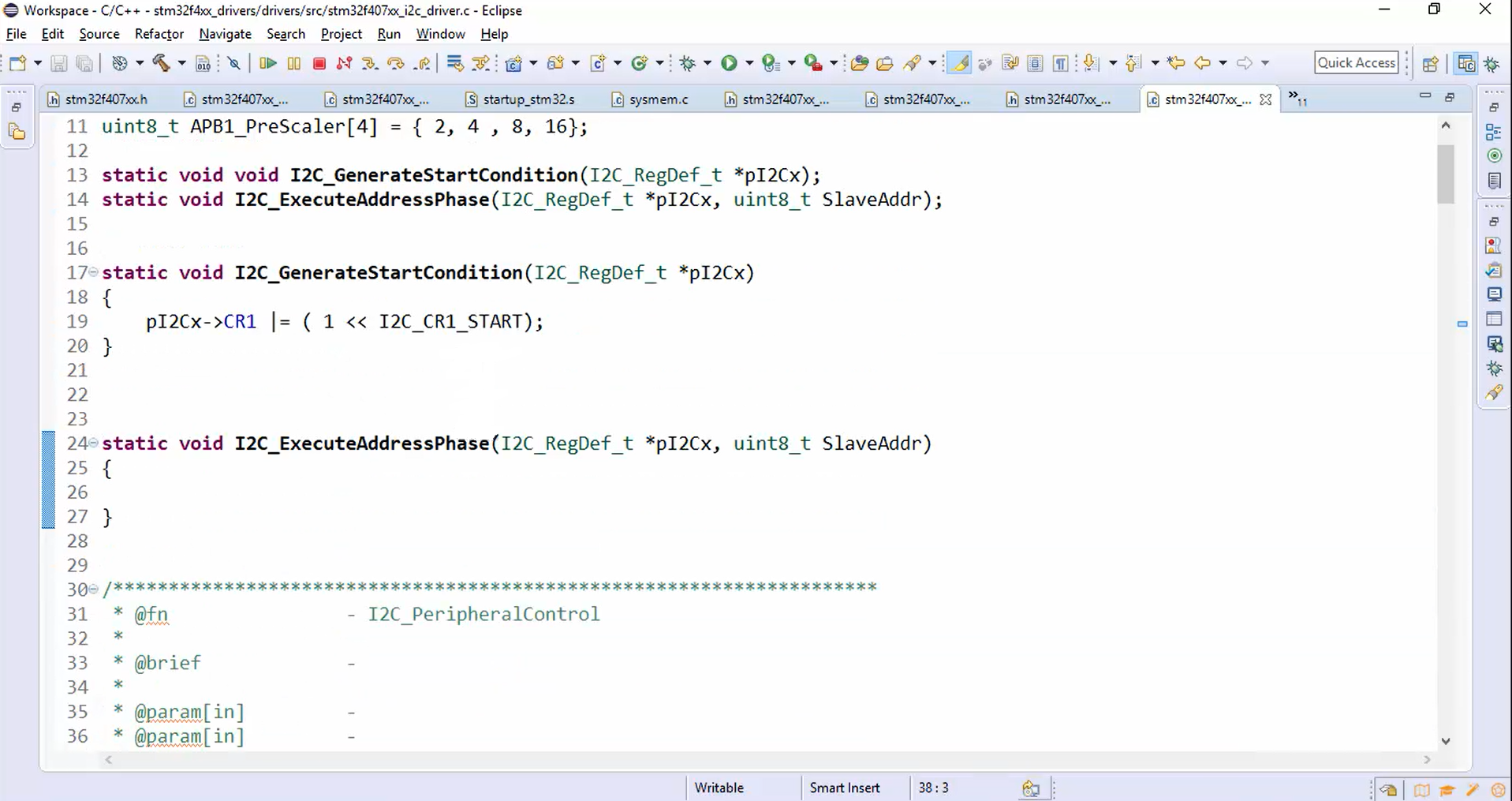
- Implement the I2C_ExecuteAddressPhase() and create its prototype at the beginning, as shown in Figure 2.
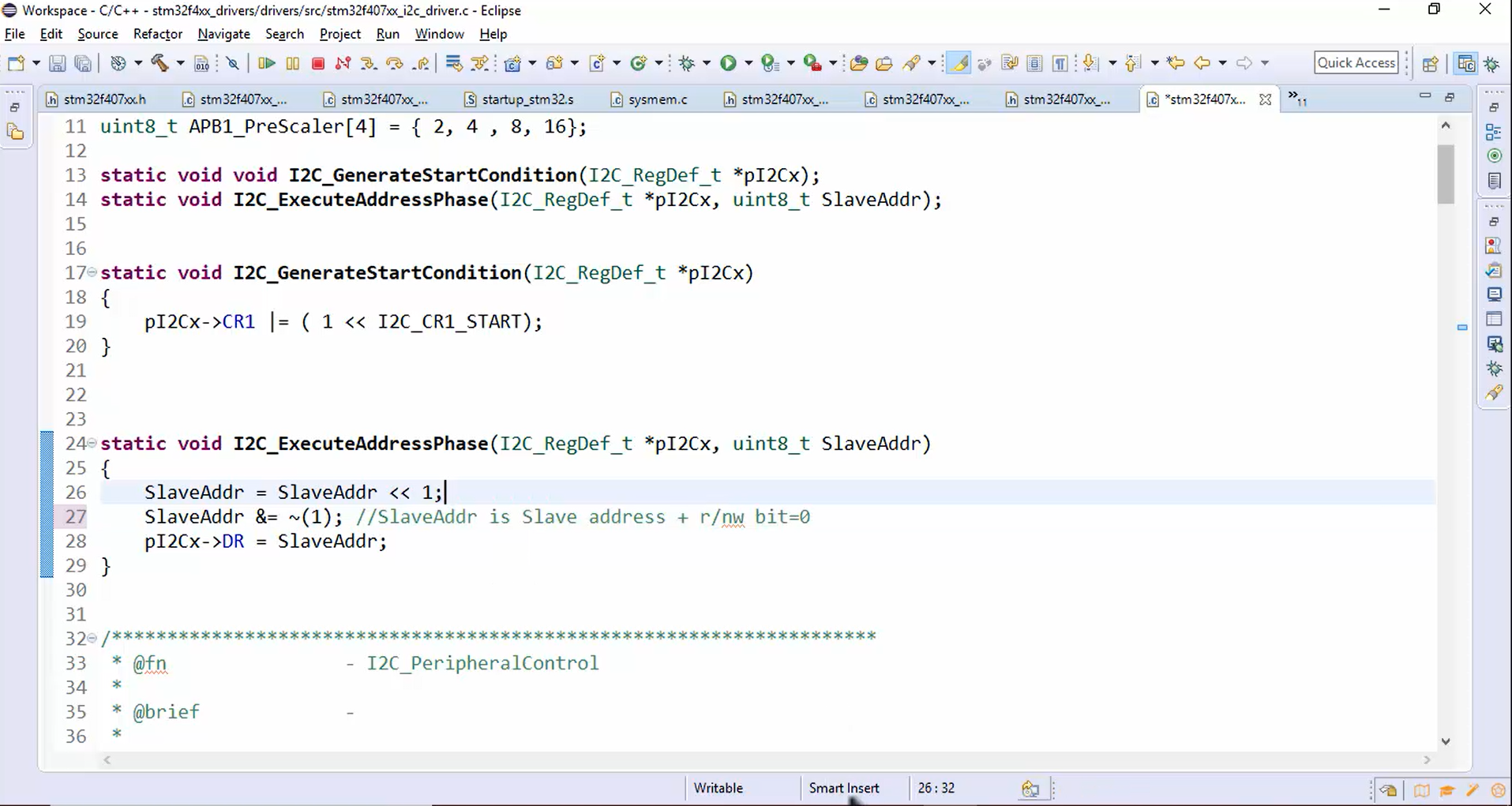
- Send a 7-bit slave address and 1-bit of read/write information (Figure 3).
- Shift the SlaveAddr by 1 bit to make the space for the read/write bit. Therefore, the 7-bit slave address is moved by 1-bit.
- Clear the 0th bit and put SlaveAddr &= ~ (1) into the data register of the I2C peripheral using pI2Cx -> DR = SlaveAddr statement. Here the SlaveAddr means the slave address + read/write bit.
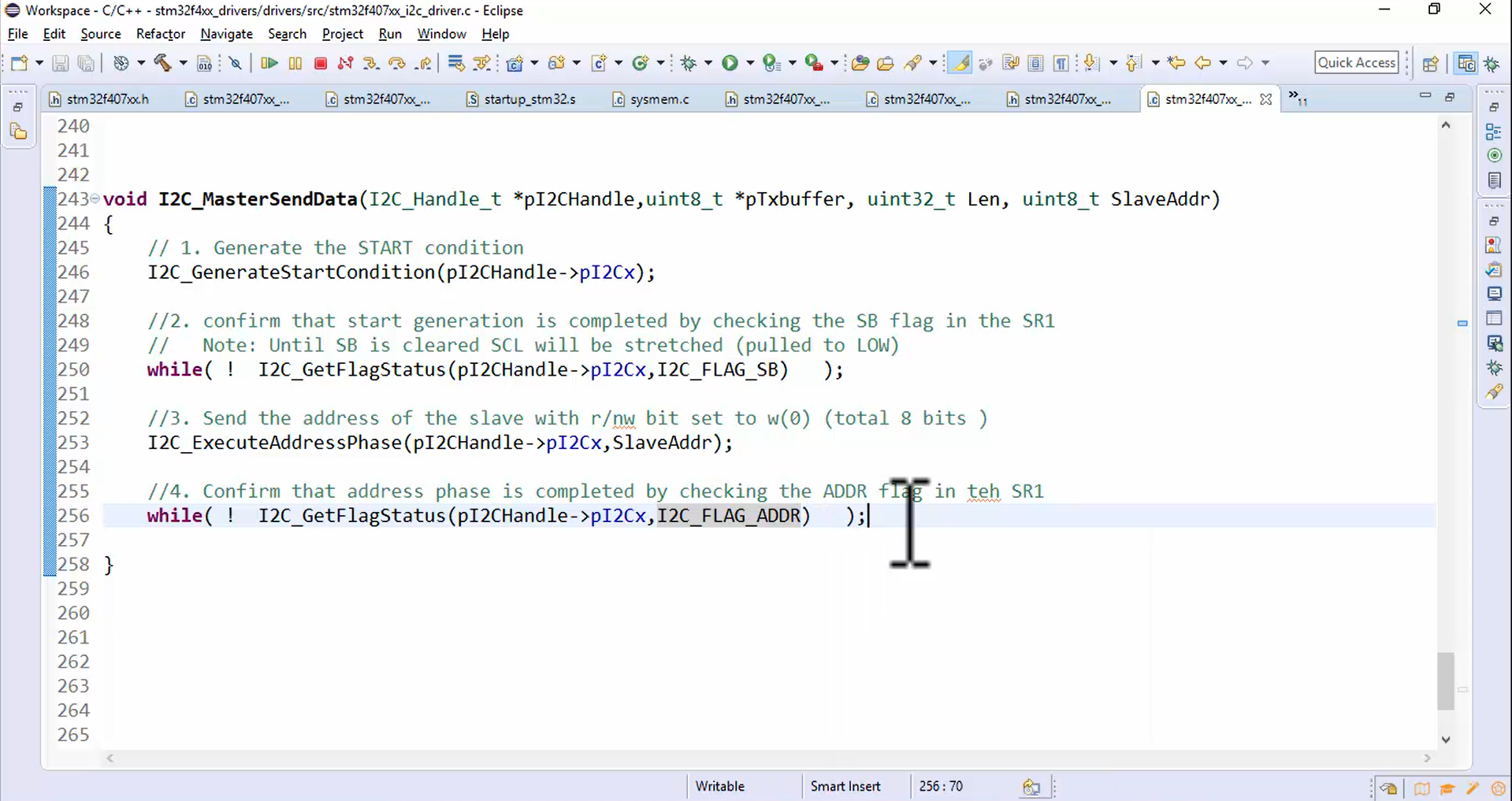
Confirm that the address phase is completed by checking the ADDR flag in the SR1 register:
- Check the ADDR flag in the SR1 register by using while statement (Figure 4).
- Ways to clear the ADDR flag is shown in Figure 5.
- ADDR is an address sent in the case of master mode, and it is address matched when the device is in slave mode.
- This bit is cleared by the software reading SR1 register followed reading SR2, or by hardware when PE=0.

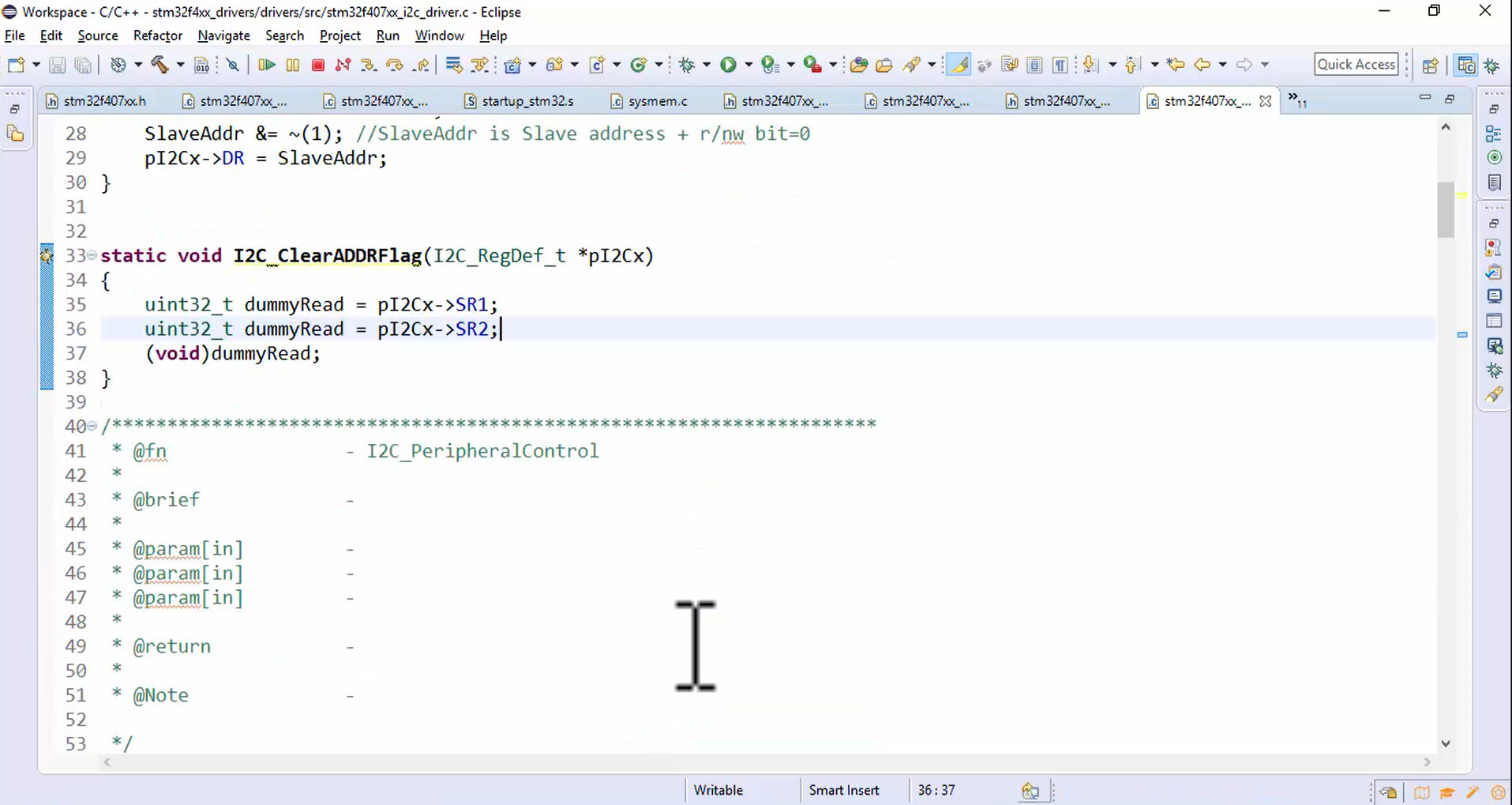
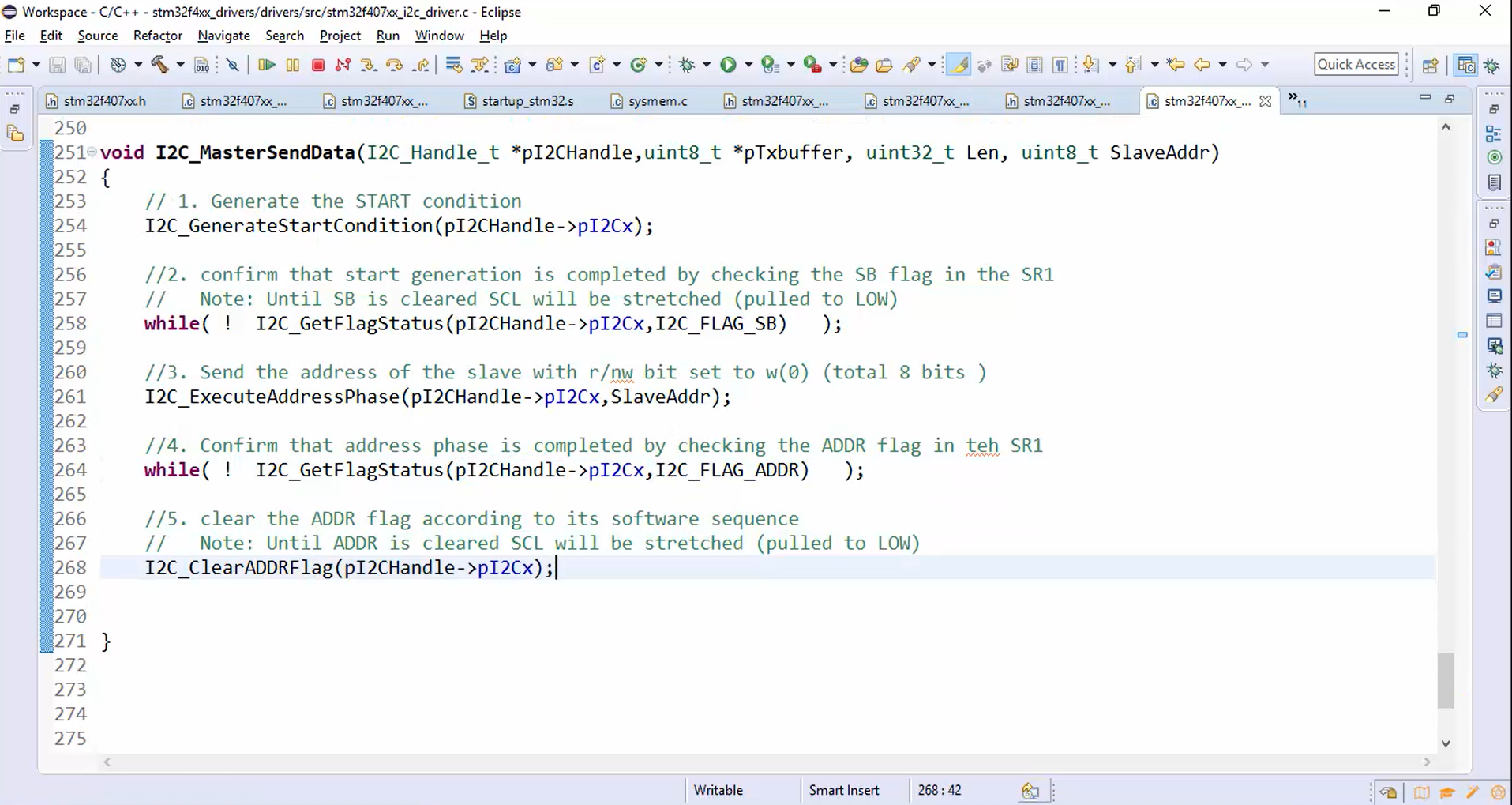
- To clear the ADDR flag, let’s create another helper function called I2C_ClearADDRFlag. Give its protocol in the beginning and implement it, as shown in Figure 6.
- First, read the SR1 followed by SR2.
- Typecast the read value to void; otherwise, the compiler will issue an unused variable error.

Figure 6. Code to implement I2C_ClearADDRFlag(). - Use the static function I2C_ClearADDRFlag() in I2C_MasterSendData function, as shown in Figure 7.
Send data until length becomes 0:
Remember that before sending the data, first confirm whether the data register is empty or not. This is done by checking the TxE flag.
FastBit Embedded Brain Academy Courses