Structure and bit fields
In this article, let’s discuss one more use case of bit fields in C.
Here is the problem statement.

Create a structure named “CarDetails” which comprises the above information. The structure should include the car’s speed, weight, color, and price. And we also know the maximum values of this information.
For example, a car’s speed maximum value could be 400, the weight maximum value could be 500 kilograms, the color is just an ASCII code, and the maximum price could be 100 million dollars.
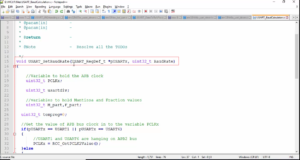
Structure without bit fields
To create a structure of that information without bit fields you can create a structure as shown in figure 2.

You use uint16 for the speed, uint16 for the weight, and select uint32 for the price. Structure without bitfields would consume 12 bytes of memory.
Since you already know the maximum values of the member elements you can also use a structure with bit fields.
Here to store the value 400 you know the maximum you would need is around 7 bits, to store the value 5000 maximum you would need 13 bits.
Structure with bit fields
So, if you know all this information, then you can go with writing a structure with bit fields where we can write something like this, as shown in Figure 3.

Here, speed, weight, and color these three variables consume 27 bits. So, 27 bits of 32 bits. So, 5 are remaining. In the remaining 5 bits, you cannot accommodate the 28 bits of information. That’s why you can split the 28 bits of information into 23 and 5. So, price_l is a price lower bits, and price_h is a price higher bits. It would take 4 + 4 = 8 bytes.
Or you can also rewrite those 2 statements(lines 25 and 26) in one single statement using uint8_t price. This will also lead to say memory consumption.
In the following article let’s discuss unions.
FastBit Embedded Brain Academy Courses
Click here: https://fastbitlab.com/course1